Contents
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Important Rulers of Delhi Sultanate
- Mamluk / Slave / Ilbari (1206-90) – 84 years
- Aibak
- Iltutmish
- Razia
- Balban
- Kaiqubad
- Khilji Dynasty (1290-1320) – 30 years
- Jalaluddin
- Alauddin
- Mubarak
- Khusru
- Tughluqs Dynasty (1320-1414) – 94 years
- Ghiyasuddin
- Muhammad bin
- Firuz Shah
- Mahmud
- Sayyids (1414-51) – 37 years
- Khizr Khan
- Alam Shah
- Lodi Dynasty (1451-1526) – 75 years
- Bahlul
- Sikandar
- Ibrahim
>>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
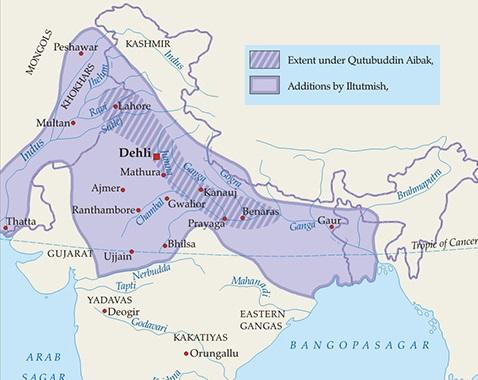
Mamluk or Slave Dynasty
Qutb ud din Aibak (1206-10)
- Muhammad of Ghori appointed Qutb ud-din Aibak as his commander.
- Qutb ud din aibak is the founder of the Mamaluk Dynasty.
- In Quranic term Mamaluk means slave.
- He prevented the Shah of Khwarizm from occupying Ghazni and Delhi.
- Qutb ud din Aibak also built Adhai Din Ka Jhonpra mosque at Ajmer.
- He built Quwwat-ul-Islam Mosque, to the north-east of minar in 1198.
- Muslim writers call Aibak Lakh Baksh or giver of lakhs because he gave liberal donations to them.
- He patronised Hasan Nizami writer of Taj-ul-Maassir.
>>>>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Iltutmish (1211-36)
- Iltutmish was sold as slave to Qutb-ud-din-Aibak and later become son-in-law of Aibak.
- He killed Aram Shah, the son of Aibak and became king in 1211.
- Iltutmish was the real founder of Turkish Kingdom in India.
- He captured Bihar and Bengal.
- Iltutmish put down the revolt of Khilji Maliks of Bengal in 1230.
- His authority recognised by Caliph of Baghdad in 1229, he received the mansur (letter of recognition).
- Iltutmish nominated his daughter Raziah as his successor before his death.
- He set up Iqta system under Iqtadars or Muqtis.
- Their duties were to lead military campaigns and maintain law and order in their Iqtas.
- Iltutmish’s army was maintained by Chahalgani or Chalisa or ‘A Group of Forty’.
- He was the first Turkish ruler to introduce Arabic coinage.
- Tanka – silver coin, an Arabic inscription on it and Jital – Copper coin.
- He patronised Minhaj-i-Siraj – writer of Tahaqqat-i-Nasuri.
>>>>>>
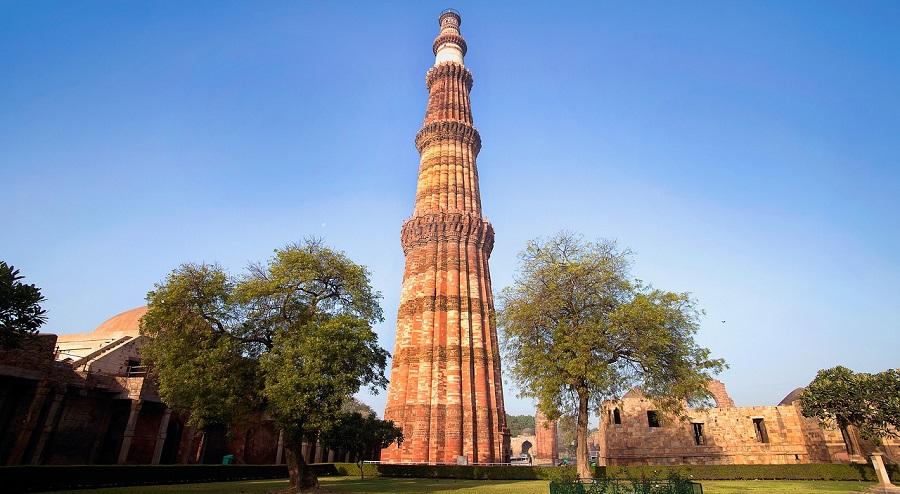
Qutub Minar
- In 1192, Qutb ud din aibak began the construction of Qutb Minar Mehrauli area in Delhi.
- Iltutmish completed the construction of the minar.
- It was named in the memory of sufi saint Qutbuddin Bakhtiar Kaki.
- It is the tallest minaret in the world made up of bricks.
- Its design is based on the Minaret of Jam, Afghanistan.
- Firoz Shah Tughlaq replaced the damaged storey, and added one more.
- Sher Shah Suri also added an entrance to this tower.
>>>>
>>>>
Rukn-ud-din (April-Nov, 1236)
- Eldest son of Iltutmish who was put on the throne by nobles.
- Another son of Iltutmish rebelled in Avadh Ruknud-din marched out of the capital to suppress the rebellion.
- This gave Raziya the opportunity to seize the throne and put her brother to death.
>>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Sultana Razia (1236-40)
- Raziah was the 1st woman only ruler of medieval India.
- She successfully restored the prestige of the Turkish Kingdom in India.
- Her rule ended in 1240 because of a conspiracy by the Turkish nobles.
- The fall of Raziya made the clique of Turkish nobles dominant in the court, and they started a scramble for supremacy.
>>>>>
>>>>
Bahram Shah (1240-42)
- Malik naib or naib-i-mamlakat, who was intended to be the de-facto ruler while the Sultan would only be a de jure ruler.
- When Bahram’s attempts to assert his authority failed, he was taken captive and put to death.
>>>>
>>>>
Alaud-din Masud (1242-46)
- Masud, son of Rukn-ud-din, was made the next Sultan.
- Balban conspired with Nasirud-din Mahmud’s mother, Malik- i-Jahan, to overthrow Masud.
>>>>
>>>>
Nasir-ud-din Mahmud (1246-64)
- He had no alternative but to leave the administration in Balban’s hands.
- In 1249 the Sultan married Balban’s daughter and made him the malik naib (regent).
- Balban was also awarded the title of Ulugh (Great) Khan.
- According to Isami’s Futuh-us-Salatin, Balban later poisoned Nasir-uddin and captured the throne.
>>>>>

delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Balban (1265-87)
- Balban believed in the Divine Right Theory of Kingship (representative of God on earth).
- He was one of the most notable of the forty Turkic nobles of Delhi, or the Chalissa.
- Balban destroyed the ‘Group of Forty’.
- He started Iranian method Sijda and Paibos (kissing his feet in the court) to the court in India.
- He also introduced the Persian festival Navroz (meaning New year).
- Balban himself called the Niyabat-i-Khudai.
- He introduced a well-organized spy system.
- A separate military department called Diwan-i-arz was established.
- Many military posts were set up at Bhojapur, Patiali, Kampil and Jalali.
- Balban suppressed Tughril Khan, who declared his independence and recovered Bengal.
- He patronized Amir Khusrau who is called as the ‘Parrot of India’ and Amir Hasan.
>>>>
>>>>
Kaiqubad
- Grandson of Balban succeeded him.
- He was soon struck with paralysis and was finally killed by the Khalji maliks.
>>>>
>>>>
Chalisa or Chalgani
- After ascending to the throne Iltutmish realised that Turkish nobles were not trustworthy.
- They could conspire against sultan to overthrow his rule.
- Therefore, Iltutmish had a group of faithful slaves to protect him.
- This group was known as Amir-i-Chahalgani or the Forty.
- They were assigned important posts and became very influential and powerful as time passed.
- After Iltutmish’s death, they became notorious and intrigued against nearly all his successors.
- They wanted to keep every new ruler under their thumb in order to keep on enjoying the full taste of power.
- Balban, one among of the Forty, assumed power.
- He fully realised that he could not become the real ruler in presence of other members of the group.
- He carefully made a plan and started to eliminate them one by one, not sparing even his cousin.
- With the elimination of the Forty, the role of the Turkish slaves in the Indian politics came to an end.
>>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Khilji Dynasty
Jalaluddin Khilji (1290-96)
- Jalaluddin Khilji was the founder of Khilji Dynasty.
- He was the first sultan to have a kind attitude towards Hindus.
- Jalaluddin Khilji avoided harsh punishments, even to those who revolted against him.
- He was also called as “Clemency Jalal-uddin” as he followed peace and wanted to rule without violence.
- Alauddin khilji was his son-in-law and also nephew.
- He appointed Ala-ud-din Khilji as the Governor of Kara.
- In 1292, Jalal-ud-din defeated the Mongols who had come up to Sunam.
- Invasion of the Yadava kingdom was done by his nephew, Ala-ud-din.
- It was the first Muslim incursions on Deccan.
- Jalal-ud-din was treacherously murdered by Ala-ud-din Khilji his son-in-law.
>>>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
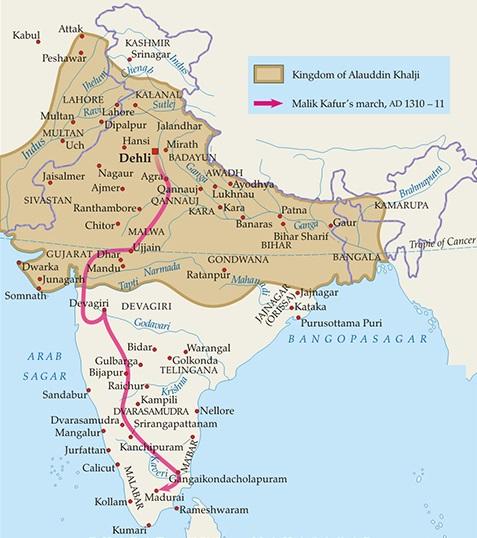
Alauddin Khilji (1296-1316)
- Alauddin khilji succeeded Jalal-ud-din Firoz Khilji.
- Alauddin khilji’s generals namely, Ulugh Khan and Nusrat Khan conquered Gujarat.
- He captured Ranthambore and killed Hamir Deva its ruler.
- In 1303 the Sultan himself marched against Chittor.
- Chittor rajputs fought valiantly, but finally the ruler, Raja Ratan Singh, submitted.
- He also captured Malwa, Dhar, Mandu, Ujjain, Marwar, Chanderi and Jalor.
- Alauddin khilji was the 1st Sultan who attacked South India.
- He sent his general Malik Kafur against the rulers of the south.
- Prataprudra-II of Warangal, Ramachandra Deva, the Yadava king of Devagiri, and Vira Ballala-III the Hoysala king were defeated.
- The kingdoms of the south acknowledged the power of Alauddin Khilji and paid his monetary tributes.
- Ala-ud-din successfully resisted the Mongol invasion more than 12 times.
- He wanted to conquer the whole world.
- Alauddin Khilji adopted the title of Sikandar-i-Sani (Alexander the Second).
- He constructed a mosque in Rameswaram.
- Alauddin khilji constructed a new capital at Siri
- He also constructed Alai Darwaza, the Palace of a thousand pillars and the Fort of Siri.
- He gave Amir Khusrau the title of Tuti-i-Hind (Parrot of India).
- Amir Khusrau and Amir Hasan was in his court.
- All grants of tax-free land and seized Muslim religious endowments.
- He banned social parties and drinking liquor (were the root causes of rebellion).
- Included non-Turks in his service.
>>>>
Military Reforms of Alauddin Khilji
- Alauddin khilji was the first to introduced a permanent standing army.
- He introduced of dagh, branding of horses.
- He also started chahra, descriptive roll of soldiers and insistence on a regular muster of the army.
- Alauddin khilji abolished the Iqtas of the royal troopers and started paying the salaries in cash.
- He organised an spy system to report all secret transactions in houses of the nobility to the Sultan.
>>>>
Market Control & Economic Reforms
- Alauddin khilji introduced strict price-control measures based on production costs.
- Merchants have to register themselves for business.
- He appointed Shahana-i-mandi (market controller), Barids (intelligence officers), and Munhias (Sultan’s secret agents).
- Established four separate markets in Delhi for separate commodities.
- Growers were ordered to sell their grain for cash in their fields at fixed prices and were not allowed to take any grain home for private sale.
- Land revenue was 50% of the gross produce and he eliminated all middle-men.
- The diwan-i-mustakhra was the new department for collection of taxes.
- Alauddin khilji started rationing system during drought or times of scarce rainfall.
>>>>>

delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Mubarak Shah (1316-1320)
- In 1315, Kafur, as regent, seized the reins of government and imprisoned Mubarak Khan.
- The Sultan gave Hasan the title Khusrau Khan and transferred Malik Kafur’s iqta and army to him.
>>>
>>>>
Khusrau Shah (1320)
- Khusrau sent an army to fight Ghazi Malik.
- Khusrau was beheaded, and Ghazi Malik ascended the throne under the title of Ghiyas-ud-din Tughluq.
>>>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Malik Kafur
- Malik Kafur was the slave general of Alauddin Khilji.
- Malik Kafur was originally a Hindu slave who fell into the hands of the Muslims at Cambay after the conquest of Gujarat.
- Alauddin’s general Nusrat Khan had paid 1,000 dinars to buy him, so Malik Kafur is also known as the “Hazardinari”.
- Sultan raised him to the position of the ‘Vazir’ or the Chief Minister for his abilities.
- Soon he was made the Commander-in-Chief of the royal forces that were sent for the conquest of the Deccan.
- Within a short time he won the Deccan states of Warangal, Dwarasamudra, Devgiri, and Madura.
- Because of this achievement his influence over Alauddin Khilji increased abnormally.
- Malik Kafur told the Sultan that his wife and sons were conspiring against him and consequently he got Malika Jahan and Alauddin’s two sons imprisoned.
- Malik Kafur got his rival and heavily punished under the orders of the Sultan.
>>>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
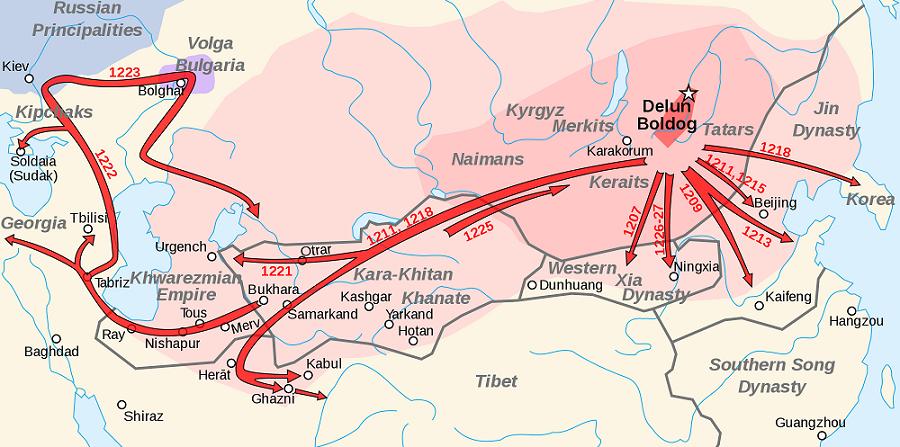
Genghis Khan (1162-1227)
- Genghis Khan was born around 1162 and first known as Temujin
- Genghis Khan was the son of the chief of the Yakka Mongols.
- When he was 10, his father was poisoned and he became chief.
- However, the tribe deserted him’ and he was forced to live alone, and survived by digging roots for food and keeping sheep.
- Three years later he was able to form alliances and organise an army.
- He became famous for his strict discipline and training and for the superiority of his army.
- Chingiz Khan invade India in 1221 and defeated Jalal ad-Din in Battle of the Indus.
- He never crossed the Indus himself.
- He was soon became the ruler of Mongolia, then set out to conquer China.
- China was made up of three main empires, Xi Xia, the Qin, and Na-Chung.
- He defeated all of them.
- Genghis Khan then moved his armies Northward, and defeated the Russian army.
- Genghis Khan’s Empire was the largest ever established.
- It extending from the Caspian Sea to the Sea of Japan, with over 700 tribes and cities under his rule.
>>>>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Tughlaq Dynasty
Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq (1320-25)
- Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq or Ghazi Malik was the founder of the Tughlaq dynasty.
- He gave more importance to postal arrangements, judicial, irrigation, agriculture, and police.
- He brought Bengal, Utkala or Orissa, and Warangal under his control.
- Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq established the city Tughlaqabad.
- In 1325 Ghiyas-ud-din was crushed to death while attending an event for his victories in Bengal.
>>>>>
>>>>>
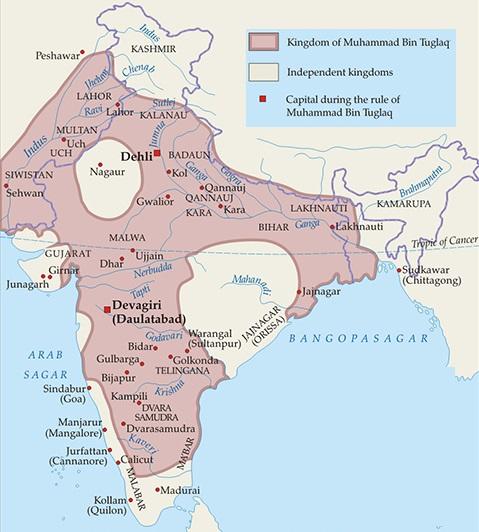
Muhammad bin Tughlaq (1325-51)
- Juna khan, (Ulugh Khan) the crown prince sworn the title Muhammad bin Tughluq.
- He was the only Delhi Sultan who had received a comprehensive literary, religious and philosophical education, as well as military training.
- Muhammad bin Tughlaq stood upright for administrative and political unity of India.
- He shifted his capital from Delhi to Devagiri (Daulatabad) to protect his capital in 1327.
- Muhammad dispatched an army to the Kangra region in (Qarachil expedition) 1329-30.
- After some initial victories in Kangra, the imperial army pressed on to Tibet, where the local hill men annihilated it.
- To fill the empty treasury, he raised taxes in the Doab region.
- Many people ran away to the forests to avoid heavy taxes.
- Due to this cultivation was neglected and severe food shortage occurred.
- Sultan has to give advance as Takkavi loans to enable the cultivators to buy seed, to sink wells, and to extend cultivation.
- An agriculture ministry called the diwan-i-kohi was established to bring barren land under cultivation.
- From 1339, he lived in a camp called ‘Svargadvari‘ for 2½ years on the bank of river Ganga.
- Sultan issued bronze (or copper) coins at par with the value of the silver tanka coins.
- The value of coins and foreign merchants naturally stopped all business dealings with India.
- Hence sultan had to withdraw the copper token currency.
- The decline of the Delhi Sultanate is claimed due to his makings of hasty decisions and out defective rules.
>>>>
>>>>
Firoz Shah Tughlaq (1351-88)
- Firoz Shah Tughlaq was the son of of Ghiyas-ud-din Tughlaq’s younger brother.
- Compensation was paid to the heirs of all those whom Muhammad had executed.
- Firoz Shah Tughlaq seized Cuttack and destroyed the Jagannatha temple at Puri.
- He established
- Department of slaves – Diwan-i-bandagan
- Department of Charity – Diwani-i-kherat
- Free Hospitals – Dar-ul-shafa
- Employment Bureau and marriage bureaus for poor Muslims
- Firoz Shah Tughlaq also set up a separate department of public works.
- He also developed royal factories called karkhanas.
- He withdrew all Taquavi (agricultural) loans granted by Mohammed-bin-Tughluq.
- Firoz Shah Tughlaq revived the Iqtadari system and made it hereditary.
- Soldiers were given land assignments, and their recruitment was made hereditary.
- He was the first Sultan to impose Sharb (irrigation tax).
- But at the same time, he built number of canals.
- He brought to an end to all unlawful and unjust taxes and collected only four types important taxes
- Kharaj- 1/10 of the produce of the land,
- Khams- 1/5 of the war booty,
- Jizya-Poll Tax,
- Zakat-Tax on Muslims for specific religious purposes
- Firoz Shah Tughlaq constructed towns like Firozabad Hissar, Jaunpur, and Fatehabad.
- He also established Diwan-i-lstibqaq to give financial aid to the poor.
- Futuhat-i-Firoz Shahi is an autobiography of Firoz Shah Tughlaq.
- He patronized scholar Zia-ud-din Barani.
- During his reign a number of Sanskrit books on medicine, science and arts were translated into Persian.
>>>>>

>>>>>
End of Tughlug Dynasty
- After Firoz’s death the sultanate disintegrated further.
- The Sharqi kingdom of Jaunpur came into existence in 1394.
- Malwa and Gujarat also broke away.
- When Timur arrived on the scene in 1398-99, the fate of the Tughluq dynasty was sealed.
>>>>
>>>>
Timur’s Invasion (1398)
- The fabulous wealth of Hindustan attracted Timur the ruler of Samarkand.
- During the period of Nasir-ud-din Mohammed Tughluq he invaded India.
- In 1398 Timur, he captured Delhi and caused annihilation by pillaging and slaughtering people.
>>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Sayyid Dynasty (1414-1451)
Khizr Khan (1414-21)
- Khizr Khan was the founder of Sayyid Dynasty.
- He was the Governor of Multan.
- Timur’s confinnation enhanced Khizr Khan’s prestige and enabled him to capture Delhi.
- In 1414 he occupied the throne of Delhi.
>>>>
>>>>
Mubarak Shah (1421-34)
- Mubarak Shah crushed the local chiefs of the Doab region and the Khokhars.
- He is first Sultan ruler to appoint Hindu nobles in the court of Delhi.
- He constructed Mubarakbad City on the banks of the river Jamuna.
>>>>
>>>>
Muhammad Shah (1434-45)
- Muhammad Shah defeated the ruler of Malwa with the help of Bahlul Lodi the Governor of Lahore.
- He conferred Bahlul Lodi with the title Khan-i-Khanan for helping in defeating the ruler of Malwa.
- He was ruling a territory which extended merely forty miles around his capital.
>>>>
>>>>
Ala-ud-din Shah (1445-57)
- When he retired to Badaun in 1447, Bahlul Lodhi captured Delhi.
- The Sultan did not contest Bahlul’s usurpation and formally transferred the sovereignty of Delhi to him in 1451.
- The Sayyids had ruled in name only.
>>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Lodi Dynasty (1451 -1526)
Bahlul Lodi (1451-89)
- Lodi dynasty was an Afghan dynasty.
- Bahlul Lodi was the founder of Lodi Dynasty.
- He never sat on the throne and he used to sit on the carpet in front of the throne with his nobles to gain their recognition and support.
>>>>
>>>>
Sikandar Lodi (1489-1517)
- Sikandar Lodi was the son of Bahlul Lodi.
- He set up a well-organized spy system.
- Sikandar Lodi developed agriculture and industry, and tried to control the market price.
- He founded Agra and shifted his capital in the year 1506.
- A work on music names “Lahjati-Sikandar Shahi” was created during his reign.
- He introduced the system of auditing the accounts.
>>>>
>>>>
Ibrahim Lodi (1517-26)
- Ibrahim Lod was an intolerant and adamant ruler.
- He had humiliated many nobles and killed some nobles cruelly.
- He also treated his son Dilwar Khan Lodi cruelly.
- Daulat Khan of Punjab and Rana Sanga of Mewar, invited Babur the ruler of Kabul to invade India.
- Babur invaded in India and defeated Ibrahim Lodi in the 1st battle of Panipat in 1526.
>>>>
>>>>
Ministers to Sultan
- Wazir – Prime Minister and Finance Minister
- Diwani-I-Risalt – Foreign Affairs Minister
- Sadr-us-Suddar – Minister of Islamic Law
- Diwan-I-lnsha – Correspondence Minister
- Diwan-I-Ariz – Defence or War Minister
- Qazi-ul-quzar – Minister of Justice
>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Land Revenue System of Delhi Sultanate
- The lands were classified into three categories
- Iqta land – Lands assigned to officials
- Khalisa land – Land under the direct control of the Sultan
- Inam land – Land granted to religious leaders or institutions.
- A class of khuts (smaller landlords) and Hindu rais (autonomous rajas) were emerged.
- Land tax Kharaj was main source of income to the state.
- Alauddin and Muhammad Tughluq took measures to fix land revenue.
- Another secular source of income to state was khams or the tax on mines, treasure-troves, etc.
- There were many other taxes, irrigation tax, grazing tax, customs and excise from traders and merchants, house-tax, etc.
>>>>>

>>>>>
Industries
- Cotton Textile Industry Increased production for new techniques, such as spinning wheel, cotton-carder’s bow and weaver’s treadles.
- Silk Industry also had an increase in the production of silk cloth due to the introduction of sericulture.
- It made India less dependent on Iran and Afghanistan for raw silk.
- Paper Industry in India was started by the Turks and there was an extensive use of paper from the 14th and 15th centuries.
- Building Industry Introduction of new techniques, like the vaulted (arched) roofing and the cementing lime, made possible large-roofed brick structures.
>>>>
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty
Literature
- The Delhi Sultans patronised learning and literature.
- Many of them had great love for Arabic and Persian literature.
- Learned men came from Persia and Persian language got encouragement from the rulers.
>>>>
Ziauddin Barani
- iauddin Barani was son of a government officer.
- He was employed at the headquarters for 17 years in the reign of Muhammad Tughluq.
- Ziauddin Barani was 74 years old when he completed his work.
- Barani’s Tarikh-i-Firuz Shahi, named after Firuz shah Tughluq.
- It begins with the first year of Balban’s reign (1266), leaving a clear gap of six years after the close of the Tabaqat-i-Nasiri, and ends with the sixth year of Firuz Shah Tugluq’s reign (1357).
- Barani wrote another book, Fatawa-i-Jahandari.
>>>>
Amir Khusrau
- Khusrau was born in 1253 in Patiala.
- Tuti-i-Hind (Parrot of India) title was given by Allauddin Khilji
- Khusrau’s father served Sultan Iltutmish in a high position.
- With his second collection of verses, Wast-uLHayat, Amir Khusrau’s name spread from house to house, wide and far and he came to be known in Persia as well.
- The famous poet of Persia, Sa’di sent him compliments.
- In Nuh Sipihr (1318), Khusrau’s fascination with India’s birds and animals, flower, its languages and people finds an impassioned expression.
- His spiritual mentor, Nizamuddin Auliya.
delhi sultanate slave khilji tughlaq sayyid lodi dynasty