Contents
Role and Functions of RBI
- The concept of RBI came from the book, “The Problem of the Rupee: its Origin and its Solution” 1923, by Dr. B. R. Ambedkar.
- The Reserve Bank of India was established on April 1, 1935 in accordance with the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- It was established based on the suggestions of “Royal Commission on Indian Currency & Finance” in 1926.
- This commission was also known as Hilton Young Commission.
>>>>>>

>>>>>>
- The Central Office of the Reserve Bank was initially established in Calcutta but was permanently moved to Mumbai in 1937.
- The Central Office is where the Governor sits and where policies are formulated.
- RBI was nationalised on 1st Jan 1949
- Financial year of RBI is from 1st July to 30th June.
- From financial year 2021-22 it will be April-March.
- A palm tree and a Tiger is the emblem of the Reserve Bank of India.
- 1935 – 1st Governor of RBI was Sir Osborne Smith.
- 1943 – 1st Indian Governor of RBI was CD Deshmukh, who participated in Bretton Woods Conference, in 1944.
- 2003 – 1st woman deputy Governor of RBI was KJ Udeshi.
- The only Prime Minister who was the Governor of RBI was Manmohan Singh.
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Central Board of Directors of RBI
- The Central Board of Directors is the administrative apex body of the Reserve Bank of India.
- The total no. of members can be a maximum 21.
- The board is appointed by the Government of India in keeping with section 8 of the RBI Act.
- Section 7 empowers the government to supersede the RBI Board and issue directions to the central bank if they are considered to be “necessary in the public interest”.
- The director of the RBI Board cannot be
- a salaried government official (except a specifically nominated member of the Government)
- be adjudicated as insolvent or have suspended payments to creditors
- an officer or employee of any bank
- found lunatic or becomes of unsound mind
>>>>>>
Official Directors of Reserve Bank of India
- Full-time directors
- 1 Governor and up to 4 Deputy Governors
- Governor and Deputy Governors hold office for max period of 5 years.
- The term of the governor may be fixed by the government at the time of his appointment.
- They are eligible for reappointment or extension as per Section 8 (4) of the Reserve Bank of India Act.
- The appointment has been made based on the recommendation of the Financial Sector Regulatory Appointments Search Committee (FSRASC), headed by the Cabinet Secretary.
- Salaries and allowances are determined by CBD, with the approval of the Central Government.
- The governor can be removed by the government of India.
>>>>>>
Non-Official Directors of Reserve Bank of India
- Nominated by the Government of India.
- Up to 10 Directors from various fields and 2 government Official
- 10 Directors hold office for 4 years, and government officials are to hold a term on RBI Board as long as the government want.
- Other 4 Directors – one each from four local boards
>>>>>>
Powers of the Central Board of Reserve Bank of India
- Board exercises all powers and does all acts and things that are exercised by the Reserve Bank of India.
- Board recommends to the government the design form, and material of bank notes and also when and where they can serve as legal tender.
>>>>>>
Meeting of Central Board of Reserve Bank of India
- Governor has to call a Board meeting at least 6 times in a year, and at least 1 each quarter.
- The meeting can be called if a min of 4 Directors ask Governor to call a meeting.
- In absence of Governor, Deputy Governor authorised by him to vote for him and presides over the Board meetings.
- In the event of split votes, Governor has a 2nd, or deciding vote.
>>>>>>
Local Boards of Reserve Bank of India
- There are one local board for each four regions of the country in Mumbai, Calcutta, Chennai, and New Delhi.
- It consists of five members each.
- Local Boards are appointed by the Central Government.
- It has a term of 4 years.
>>>>>>
Enforcement Department
- It started in 2017.
- It will enforce all laws to the banks or others as per surveillance from different departments of RBI.
>>>>>>>>
>>>>>>>>
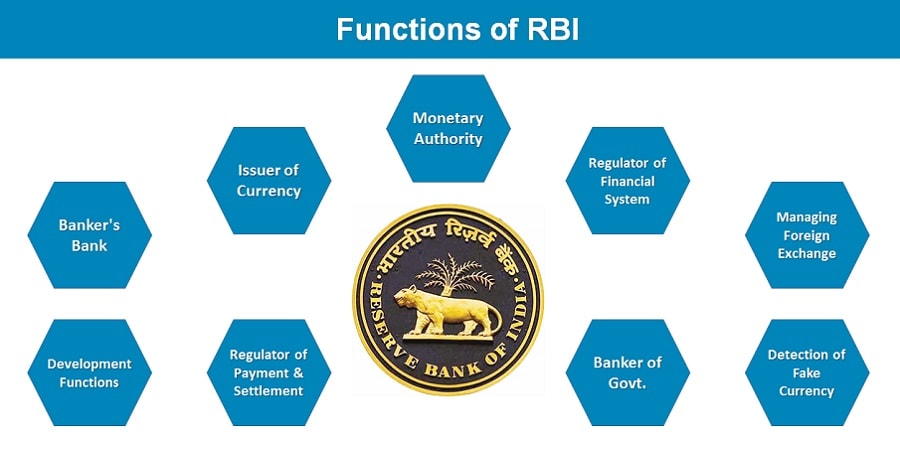
Role & Functions of RBI
Monetary Authority
- The main functions of RBI are to formulate, implement and monitor the monetary policy.
- Target of monetary policy
- Maintaining price stability, keeping inflation in check
- Ensuring adequate flow of credit to productive sectors
>>>>>>
Regulator & Administrator of the Financial System
- The Reserve Bank of India controls the monetary supply in India.
- It monitors economic indicators like the GDP, CPI etc.
- Decide the design of the rupee banknotes as well as coins.
- RBI is to undertake supervision of the financial sector comprising commercial banks, financial institutions and non-banking finance companies.
- Banking Ombudsman Scheme has formulated by Reserve Bank of India for consumer Complaints.
- RBI lays out parameters of banking operations within which all the banking and financial system functions for
- maintaining public confidence in the system
- protecting depositors’ interest
- providing cost-effective banking services to the public
>>>>>>
Managing Foreign Exchange
- Reserve Bank of India manages Forex under the FEMA- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999.
- Facilitate external trade and payment.
- Promote the development of foreign exchange market in India.
>>>>>>
Issuer of Currency
- Reserve Bank of India is authorized to issue currency in India except Rs.1 notes.
- One rupee notes printed by the Ministry of Finance.
- The bank also destroys the same when they are not fit for circulation.
- All the money issued by the central bank is its monetary liability.
- Security Printing and Minting Corporation of India Limited (SPMCIL), prints note for RBI.
- It is a wholly owned company of the Govt. of India.
- SPMCIL has 2 printing presses at
- Nashik, Maharashtra
- Dewas, MP
- Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran Private Limited (BRBNMPL), also has set up printing presses
- Mysore in Karnataka
- Salboni in West Bengal
- SPMCIL has 4 mints for coins
- Mumbai
- Alipore (Kolkata)
- Hyderabad
- NOIDA (UP)
- Govt. of India has the sole right to mint coins as per the Coinage Act, 1906.
>>>>>>
Developmental Functions of RBI
- Reserve Bank of India faces a lot of inter-sectoral and local inflation-related problems.
- Key tools in this effort is Priority Sector Lending.
- RBI work towards strengthening and supporting small local banks.
- Encourage banks to open branches in rural areas to include large section of society in banking network.
>>>>>>
Regulator of the Payment & Settlement Systems
- Payment and Settlement Systems Act of 2007 (PSS Act) gives the RBI authority, including regulation and supervision, for the payment and settlement systems in the country.
- In this role, the RBI focuses on the development and functioning of safe, secure and efficient payment and settlement mechanisms.
- Two payment systems NEFT and RTGS managed by Reserve Bank of India.
>>>>>>
Banker & Debt Manager to Government
- As a banker to the GoI, RBI maintains its accounts, receive payments into & make payments out of these accounts.
- RBI also helps GoI to raise money from public via issuing bonds and govt. approved securities.
>>>>>>
Banker’s Bank
- It works as a central bank where commercial banks are account holders and can deposit money.
- Reserve Bank of India maintains banking accounts of all scheduled banks.
- It is the duty of the Reserve Bank of India to control the credit.
- The RBI also advises the banks on various matters for example Corporate Social Responsibility.
>>>>>>
Detection of Fake Currency
- Reserve Bank of India has launched a website to raise awareness among masses about fake notes.
>>>>>>>>

>>>>>>>>
Reserves of RBI
Foreign Exchange Reserve (Forex Reserve) of India
- Foreign Currency Assets
- Gold
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs)
- Reserve Tranche Position
>>>>>>
Special Drawing Rights (XDR)
- Special Drawing Rights is a supplementary foreign-exchange reserve assets defined and maintained by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- The XDR is the unit of account for the IMF, and is not a currency.
- Special Drawing Rights was created in 1969 to supplement a shortfall of preferred foreign-exchange reserve.
- XDR basket consists of
- USD
- Euro
- Renminbi (Chinese yuan)
- Japanese yen
- British pound
>>>>>>
Reserve Tranche Position (RTP)
- Reserve Tranche Position is the difference between a member’s quota and the IMF’s holdings of its currency.
- It is an emergency account that IMF members can access without agreeing to conditions or service fee at any time.
>>>>>>
Asset Development Fund
- Asset Development Fund was created in 1997-98.
- It helps to meet the internal capital expenditure and new investments in RBI’s subsidiaries and associate institutions.
>>>>>>
Currency & Gold Revaluation Reserve (CGRA)
- The CGRA is meant to cover a situation where
- Rupee appreciates against one or more of the currencies in the basket
- There is a decline in the rupee value of gold
- The basket has several currencies ranging from the dollar to the euro and the yen.
- The level of CGRA now covers about a quarter of the total currency reserves of the Reserve Bank of India.
>>>>>>
Contingency Fund Reserve of RBI
- It used to cover depreciation in the value of the RBI’s holdings of government bonds domestic and foreign.
- It used when yields rise and their prices fall.
- To cover expenses from extraordinary events such as demonetization, money market operations, and currency printing expenses in a year of insufficient income.
- This reserve supports the mother of all guarantees – central bank’s role as the lender of the last resort.
- It covers the deposit insurance for Deposit Insurance and the Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) a subsidiary of Reserve Bank of India.
