Contents
national income gdp full form gross product methods for measuring disposable
National Income
- “National income accounting is a set of rules and definitions for measuring economic activity in the aggregate economy.” D.C. Colander
- It tries to summarise the performance of an economy by measuring national income aggregates in a year.
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Uses of National Income Accounting
- National income indicates the performance of the economy of a country.
- Govt. can identify economy’s strength and failures.
- Govt. can formulate new policy depend on the result.
- National income accounting helps to evaluate and review of policies under implementation.
- It reflect the specific contribution of individual sectors and their growth over time
- Accounting helps to reflect how national income is shared among various factors of production
- It helps in making comparison among nations in respect of national income and per capita income
- It is helpful to UNO which formulates welfare plans for different countries
CSO – Central Statistics Office
- It is under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
- CSO is responsible for co-ordination of statistical activities in India
- Most of the statistical data prepared by CSO like, GDP, National Income, Inflation etc.
- Established in 1951 in Delhi
- It has two publications
- The statistical abstract – In India (annual)
- The monthly abstract of Statistics
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Concepts in National Income and Output
Gross Domestic Product – GDP
- It refers to the money value of all finished goods & services produced within country for a given time period.
- GDP is a broad measurement of a nation’s overall economic activity
- Gross would mean we are considering the amount of goods without deducting depreciation
- GDP came into use in 1937 in a report to the U.S. Congress by economist Simon Kuznets in response to the Great Depression
- It includes the productions within
- Political frontiers of country
- Territorial waters of the country
- Embassies, consulates and military establishments in abroad
- Ships and aircraft operated by the residents of the country with other countries
- Engaged in extraction in areas in which the country has exclusive rights of exploitation
- Base year for GDP in India is 2011-12.
Nominal GDP or GDP at Current Prices
- Nominal GDP is the present market value of goods and services produced in a country during a year.
- It will include all of the changes in market prices that have occurred during the current year due to inflation or deflation.
- It is also called as GDP as market price.
Real GDP or GDP at Constant Prices
- Real GDP is an inflation-adjusted measurement of value of all goods and services produced by an economy in a given year
- It is expressed in base-year prices.
GDP Deflator
- GDP deflator or implicit price deflator is a measure of the level of prices of all new, domestically produced, final goods and services in an economy in a year.
- GDP deflator = (Nominal GDP / Real GDP) X 100
- It is a measure of price inflation/deflation with respect to a specific base year
- The Gross Domestic Product deflator of the base year itself is equal to 100.
- GDP deflator is not based on a fixed basket of goods and services
- The “basket” for the GDP deflator is allowed to change from year to year with people’s consumption and investment patterns
national income gdp full form gross product methods for measuring disposable
Nominal GDP vs. Real GDP
- Nominal Gross Domestic Product is based on the monetary value of goods and services, it is subject to inflation.
- Real GDP is calculated using a GDP price deflator, which is the difference in prices between the current year and the base year.
- Nominal GDP is used when comparing different quarters of output within the same year. When comparing the GDP of two or more years, real GDP is used.
- Overall, real GDP is a much better index for expressing long-term national economic performance.
GDP at Factor Cost
- If we deduct total indirect taxes and add total subsidies to GDP at market price we will get GDP at factor cost.
- GDP at factor cost = GDP at market price – Tax + Subsidies
national income gdp full form gross product methods for measuring disposable
Net Domestic Product – NDP
- NDP accounts for capital that has been consumed over the year in the form of housing, vehicle, or machinery deterioration.
- Net Domestic Product = GDP – Depreciation
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Gross National Product – GNP
- It is an estimate of total value of all the final output of products and services in a time period by a country’s residents.
- GNP = Consumption + Government Expenditures + Investments + Exports + Factor Income of Indians abroad – Factor Income of foreigners in India
- GNP = GDP + Net Factor Income from abroad
- Net Factor Income from abroad = Factor Income of Indians abroad – Factor Income of foreigners in India
- Gross National Product is citizen specific, not location specific
- GNP includes total money value of goods and services produced by Indians and Indian entities
GDP vs GNP
- GDP looks at the value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders, GNP is the market value of goods and services produced by all citizens of a country
- GDP is an indicator of the local/national economy, GNP represents how its nationals are contributing to the country’s economy.
Net National Product – NNP
- It refers to the total market value of all final goods and services produced by the factors of production by the citizen of a country during a given time period, minus depreciation.
- Net National Product can also be found out by adding the Net Factor Income from abroad to the NDP
- NNP at Market price = GNP – Depreciation
- NNP at Market price = Net domestic product + Net Factor Income from abroad
Net National Income or NNP at factor cost
- It can be defined as the net value added at factor cost (by the citizen) in an economy during an accounting year.
- It is the income earned by the factors of production by citizen of a country.
- NNP at factor cost or national income is defined as the sum of domestic factor incomes and Net Factor Income from abroad.
- If NNP figure is available at market prices indirect taxes must be subtracted and subsidies added to get NNP at factor cost or national income.
- NNP at Factor cost = Net National Income = NNP at market price – Tax + Subsidies
National Disposable Income
- National Disposable Income = NNP at Market price + Current transfers from the rest of the world
- Current transfers = Net Remittance + Gifts + Aid etc.
Personal Income
- It is the sum of all incomes actually received by individuals of a country during a given year.
- In order to estimate it, from national income
- Personal Income = Net National Income – Sum of social security benefits – Corporate income – Corporate taxes – Undistributed corporate profits + Personal payments
- Personal payments are kind of payment not for any production, for other reasons
- Example of personal payments – Pension, Student scholarships
national income gdp full form gross product methods for measuring disposable
Personal Disposal Income
- It refers to the amount of money that households have available for spending and saving after income taxes.
- Personal disposable income equal to consumption plus saving
- Personal Disposal Income = Personal Income – Taxes = Consumption + Savings
Purchasing Power Parity – PPP
- It is a theoretical exchange rate that allows you to buy the same amount of goods and services in every country.
- Purchasing power parity is a theoretical rate because no country actually uses it.
- But government agencies use it to compare the output of countries that use different exchange rates.
- The World Bank computes PPP for each country.
- It provides a map that shows the PPP ratio compared to the United States.
national income gdp full form gross product methods for measuring disposable
>>>>>>
Methods for Measuring National Income
- There are mainly 3 methods to measuring national income
- Product or Gross Value Added Method
- Income Method
- Expenditure Method
Value Added (GVA) or Product Method
- This is also called output method.
- In this method the value added by each firm in the production of goods and services is measured.
- Value added by a firm is measured by deducting expenditure incurred on intermediate goods such as raw materials, industrial product or services.
- From the value added by each firm we subtract consumption of fixed capital (depreciation) to obtain net value added at basic prices.
- GVA at Basic price = Value added of all sectors production – Intermediate consumption
- GDP at Market price = GVA at basic price + Product tax – Product subsidies
- GVA at basic prices will include production taxes and exclude production subsidies available on the commodity.
- GVA at Factor Cost = GVA at basic price – Production taxes + Production subsidies
- In this method, the economy is divided into different economic sectors such as agriculture, industry and service.
- We need to add all the sectors and sub-sectors value added to get GDP.
- Some other things should be in mind while using this method
- Rent values of self-occupied houses should be included
- Value of production for self-consumption should be counted. Ex – agricultural products
- Brokerage or commission should be counted
- Sale and purchase of second-hand goods should not be included
- Value of services of housewives are not included
national income gdp full form gross product methods for measuring disposable
Merits and Demerits of Value Added Method
- GVA gives a picture of the economic activities from the producers’ side or supply side
- A sector-wise output provided by the GVA, which help the policymakers to decide to formulate sectors-wise policy.
- Problem of double counting arises due to the fact that the industry’s output is often the input of another industry
Income Method
- We add all the incomes from employment and ownership of assets before tax, received from all the production activities in an economy.
- This method approaches national income from distribution side.
- It also includes interest on capital, profits of entrepreneurs and trading surplus of the public sector corporations.
- In this method identify the productive firms and then classify them into various economic sectors.
- Factor payments are classified into the following groups
- Wages, salaries and social security schemes of employees
- Rent and royalty
- Interest
- Profits
- Dividends
- Undistributed profits
- Corporate income tax
- Mixed income of the self-employed
- By summing up the incomes paid out by all sectors we can get domestic factor income
- It is also called net domestic product at factor cost.
- GDP at market price = Total Factor Cost + Tax – Subsidies
- Factor costs
- Land – Rent
- Labour – Wages
- Capital – Interest
- Entrepreneur – Profit
- Total Factor Cost = Rent + Wages + Interest + Profit
>>>>>>>

national income gdp full form gross product methods for measuring disposable
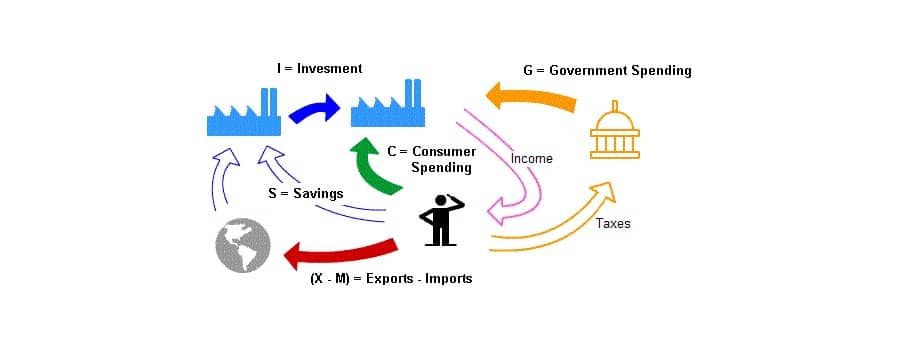
Expenditure Method
- This method measures the total domestic expenditure of the economy.
- Expenditure is two types consumption expenditure and investment expenditure.
- GDP at Market Price = Final Private Consumption + Investment + Govt. purchase + Net Export (Export – Import)
- Real GDP = GDP at market price need to adjusted with base year
- Expenditure method gives a picture of the economic activities from the consumer side.
Final Private Consumption
- It is the money spend by consumer to buy consumption of goods and services
- Consumer spending is the biggest component of GDP
- Intermediate consumption is not counted
- New house or property purchased will be counted in investment (Not as Private Consumption)
Investment
- Investment is private domestic investment, or capital expenditures.
- Business investment increases productive capacity and boosts employment and GDP.
- Such as new house, Share, Bond, Debenture or any goods that will be used in future production will be counted
Government Purchase
- Government purchase is consumption expenditure and gross investment.
- Govt. spend money on equipment, infrastructure, and salary.
- Ex- FCI food grain purchase, LPG-DBT, pension, scholarship, road, railways construction etc.
Net Export
- Net Export = Exports – Imports
- A current account surplus boosts a nation’s GDP, while a deficit is a drag on GDP.
- Export includes Indian and foreign companies operating in India
Residual Error
- All these methods of measuring national income are supposed to give the same final figure.
- Any mismatch among the three measures is due to statistical and calculation error.
- This is known as rounding-up error or residual error.
Major Difficulties in Measurement
- Non-availability and unreliability of accurate data relating to the various sectors of the economy
- Double Counting problem in excluding raw materials and semi-finished goods from the estimates of national income
- Difficulties in making proper adjustment of the changes in the price-level or inflation
- Proper value of public goods like road, hospitals, defence, schools are unknown.
- Self-Supplied Goods and Services. Ex- owner-occupied houses, farmers produce food for themselves
National Income Doesn’t Cover
- Underground Economy
- Non-Marketed Activities (Mom cooking food for home)
- Barter Exchanges (Rice given for oranges)
- Informal sector income
- Negative Externality (3rd party effected by any productivity)
- Ex- environmental problems
- Opportunity cost
- Income Inequality (Gini Coefficient)
>>>>>>>