Contents
>>>>>>>
Drainage Systems Based on Origin
Himalayan Rivers
- Those are Perennial rivers
- The Indus river, the Ganga river, the Brahmaputra river and their tributaries.
>>>>>>
Peninsular Rivers
- Those are Non–Perennial rivers
- Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna, the Cauvery, the Narmada and the Tapi and their tributaries.
>>>>>>

>>>>>>>
Based on Orientation to the Sea
Bay of Bengal Drainage
- Rivers that drain into Bay of Bengal.
- They are East flowing rivers
- 77% of the drainage area of the country is oriented towards Bay of Bengal
- 90% of the water drains into the Bay of Bengal
>>>>>>
Arabian Sea Drainage
- Rivers that drain into Arabian sea
- They are West flowing rivers.
- 23% of the drainage area of the country is oriented towards Arabian sea
- Less than 10% of the water drained into the Arabian Sea
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Himalayan River Systems
- The Indus river, the Ganga river and the Brahmaputra river comprise the Himalayan river systems.
- Himalayan Rivers existed even before the formation of Himalayas (Antecedent Drainage)
- They were flowing into the Tethys Sea.
- Himalayan Rivers had their source in the now Tibetan region.
- The deep gorges of Indus rive, Satluj river, Brahmaputra river etc. indicate that these rivers are older than the Himalayas.
- They continued to flow throughout the building phase of the Himalayas
- Their banks rising steeply while the beds went lower and lower due to vertical erosion
- In upper reaches (Youthful stage) they form Gorges, V-shaped valleys, rapids, waterfalls, truncated spurs etc.
- In plain areas or middle part (Mature stage) they form depositional features like flat valleys, ox-bow lakes, flood plains, braided channels, and deltas near the river mouth.
- Over the plains, Himalayan Rivers display a strong meandering tendency and shift their courses frequently
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Evolution of the Himalayan River System
- A mighty river called Shiwalik or Indo-Brahma traversed the entire longitudinal extent of the Himalaya from Assam to Punjab and onwards to Sind
- It discharged into the Gulf of Sind near lower Punjab
- It was during the Miocene period some 5-24 million years ago.
- Evidences – The remarkable continuity of the Shiwalik and its lacustrine origin and alluvial deposits consisting of sands, silt, clay, boulders and conglomerates support this viewpoint.
- It is opined that in due course of time Indo–Brahma river was dismembered into three main drainage systems
- Indus river and its five tributaries in the western part;
- Ganga river and its Himalayan tributaries in the central part
- Stretch of the Brahmaputra river in Assam and its Himalayan tributaries in the eastern part.
- The dismemberment was probably due to the Pleistocene upheaval in the western Himalayas
- It includes the uplift of the Potwar Plateau (Delhi Ridge)
- Potwar Plateau acted as the water divide between the Indus river and Ganga river drainage systems.
- Malda gap is the area between the Rajmahal hills and Meghalaya plateau
- It diverted the Ganga river and the Brahmaputra river systems to flow towards the Bay of Bengal.
- During the mid-pleistocene period it came into excessed
>>>>>>
>>>>>>>
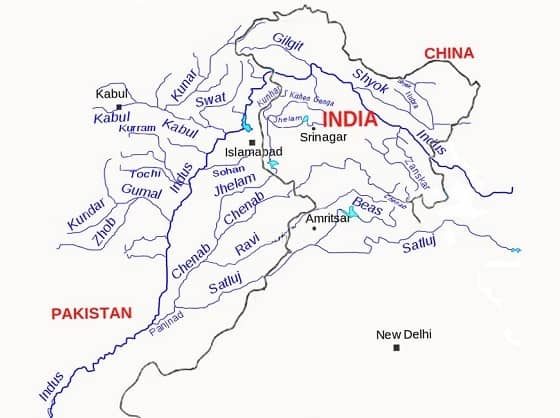
Indus River
- India got her name from the Indus river.
- Source – Lake Manasarovar (5180 m) of Kailas Range, Tibet
- Length is about 2,880 km
- Right Tributaries – Shyok, Hunza, Gilgit, Kabul, Kurram, Gomal
- Left Tributaries – Zanskar, Suru, Soan, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, Sutlej, Panjnad
- Indus river is joined by the Dhar River near the Indo-China border.
- Indus is an antecedent river system.
>>>>>>
Right Bank Tributaries of Indus River
Shyok River
- It mean The River of Death
- Source – Rimo Glacier
- Length – 550 km
- Shyok River joins Indus river at Keris, to the east of the town of Skardu
- Statue of Maitreya Buddha facing down the Shyok River
- Tributaries – Chang Chen Mo, Galwan, Nubra, Saltoro
>>>>>>
Hunza River
- Principal river of Gilgit–Baltistan region.
>>>>>>
Gilgit River
- Source – Shandur Lake
- Gilgit river joins the Indus River at junction point of three mountains ranges near town of Juglot
>>>>>>
Kabul River
- Source – Hindu Kush, Afghanistan
- Joins Indus river near Attock
Gomal River
- Source – Katawaz Region, Afghanistan
>>>>>>

>>>>>>
Left Bank Tributaries of Indus River
Zanskar River
- Zanskar river joins the Indus river near “Nimmu” in Ladakh
>>>>>>
Suru River
- Source – Panzella glacier, Pensi La Kargil
- Join with the Indus River at Nurla
- Kargil town is situated on the banks of it
- A branch of the ancient Silk Road ran alongside the Suru River
>>>>>>
Jhelum River (Vitasta / Hydaspes)
- Source – Verinag Spring in the south-eastern part of the Kashmir Valley
- Jhelum river flows northwards into Wular Lake
- It forms steep-sided narrow gorge through Pir Panjal Range below Baramula.
- Jhelum river forms the India–Pakistan boundary for 170 km
- It joins the Chenab at Trimmu.
- Kishanganga, is a tributary of Jhelum river.
>>>>>>
Chenab River (Chandrabhaga River)
- Source – Bara Lacha Pass, Himachal Pradesh
- Chenab river formed by the confluence of two rivers, Chandra and Bhaga.
>>>>>>
Ravi River (Iravati )
- Source – Kullu hills near Rohtang Pass, Kangra district, Himachal Pradesh.
- Ravi river debouches into the Chenab a little above Rangpur
- Ujh is a tributary of Ravi river
>>>>>>
Beas River (Vipasa)
- Source – Beas Kund, near Rohtang Pass, Himachal Pradesh
- Beas river meets the Satluj river at Harike in Punjab.
- It lies entirely within the Indian territory
- Beas river marks the eastern-most border of Alexander the Great’s conquests
>>>>>>
Sutlej River (Shatadrum)
- Source – Manasarovar-Rakas Lakes in Tibet at a height of 4,570 m within 80 km of the source of the Indus river.
- Tibetan name Langqên Zangbo mean Elephant River
- Sutluj river forms the boundary between India and Pakistan for nearly 120 km.
>>>>>>
Panjnad River
- Jhelum and Ravi join Chenab, Beas joins Sutlej, and then Sutlej and Chenab join to form Panjnad 10 miles north of Uch Sharif in Muzaffar Garh district
- Length – 71 km
- Sources – Chenab River, Sutlej, Ravi River, Jhelum River, Beas River
- Panjnad river joins the Indus river a few kilometres above Mithankot.
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Indus Water Treaty
- Water-distribution treaty between India and Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank.
- Signed in Karachi on Sept 19, 1960 by Jawaharlal Nehru and President of Pakistan Ayub Khan.
- Eastern rivers of India – the Beas, the Ravi and the Sutlej given to India.
- Western rivers of India – the Indus river, the Chenab and the Jhelumgiven to Pakistan.
- India can use nearly 20% of the total water carried by the Indus river system.
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
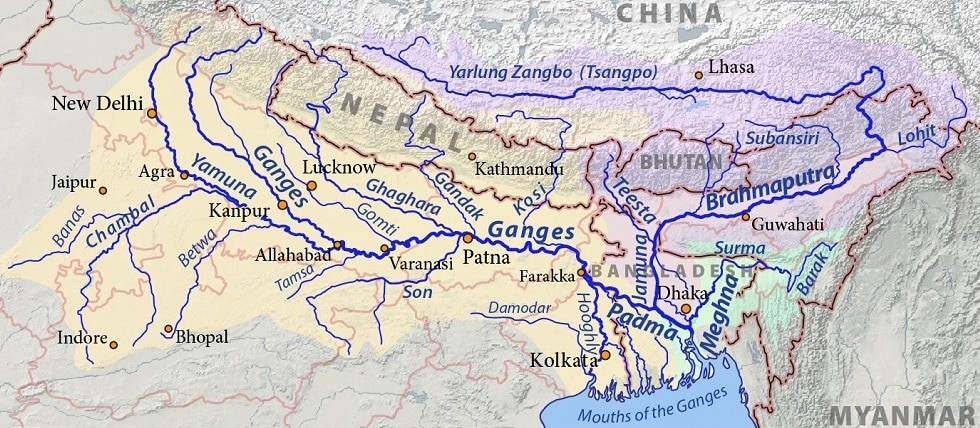
Ganga River
- Source – Gangotri glacier (7,010 m), Uttar Kashi District, Uttarakhand.
- Lenth is 2,525 km in India.
- Alaknanda River joins Bhagirathi river at Devaprayag.
- From Devapryag the river called as Ganga river.
- Ganga river enters the plains at Haridwar.
- Ganga river is one of the most polluted river of the world.
- Pollution threatens many fish species and amphibian species and the endangered Ganga river dolphin (Blind Dolphin).
- Near Rajmahal Hills it turns to the south-east.
- At Farraka, Ganga river bifurcates into Bhagirathi-Hugli in West Bengal and Padma-Meghna in Bangladesh
- Brahmaputra river joins Padma-Meghna in Bangladesh.
- Gangetic dolphin is the National Water Animal of India
- Left Tributaries – Alaknanda, Ramganga, Gomti, Ghaghara, Gandak, Kosi, Mahananda
- Right Tributaries – Yamuna river, Tamsa river, Son, Punpun
>>>>>>
>>>>>>>
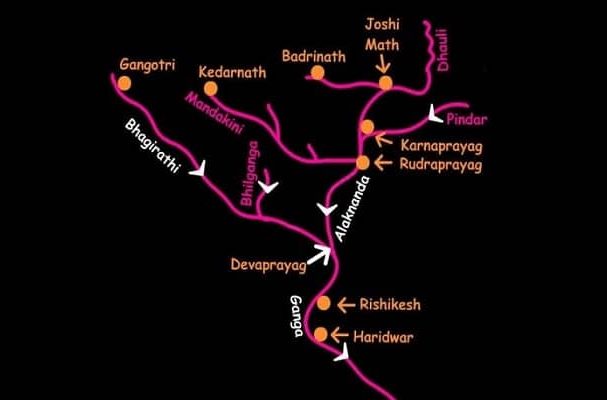
Alaknanda River
- Source – Satopanth Glacier
- Several rivers in the Garhwal region merge with the Alaknanda river at places called Prayag or ‘holy confluence of rivers
- Vishnuprayag – met by the Dhauliganga River
- Nandaprayag – met by the Nandakini River
- Karnaprayag – met by the Pindar River
- Rudraprayag – met by the Mandakini or Kali ganga
- Devprayag – meets the Bhagirathi River
>>>>>>
Yamuna River
- Largest and the most important tributary
- Source – Yamnotri glacier (6330 m) Bandarpunch Peak in the Garhwal region, Uttarakhand
- Length – 1,376 km
- Yamuna river unites with Ganga river near Triveni Sangam, Allahabad.
- Its main affluent in the upper reaches is the Tons which also rises from the Bandarpunch glacier.
- Tons river joins Yamuna river below Kalsi before the latter leaves the hills.
- Left bank tributaries – Hindon, Sharda, Giri, Rishiganga, Hanuman Ganga, Sasur Khaderi
- Right bank tributaries – Chambal, Betwa, Ken, Sindh, Tons
>>>>>>
Important Tributaries of Yamuna River
Chambal River
- Source – Janapav Hills (700 m), Vindhyan Range, MP
- Chambal river flows through the Malwa Plateau.
- It joins Yamuna river in Etawah district of Uttar Pradesh.
- Chambal river flows much below its banks due to severe gully erosion.
- Chambal Valley, giving rise to badland topography.
- Keoladeo National Park is supplied with water from Chambal river irrigation project.
- Left tributary – Banas, Mej
- Right tributary – Parbati, Kali Sindh, Shipra
Important Tributary of the Chambal River
Banas River
- Source – Aravalli Range
- Banas river joins the Chambal river on Rajasthan – Madhya Pradesh border near Sawai Madhopur.
>>>>>>
Shipra River
- Source – Kakri Bardi Hills
- Kumbh Mela takes place on Ujjain river-side ghats
>>>>>>

>>>>>>
Tons River
- Source – Bandarpunch, Uttarakhand
- It joins Yamuna river at Dehradun, Uttarakhand
- Length – 150 km
>>>>>>
Betwa River
- Source – Vindhyan Range, Bhopal, MP
- Betwa river joins Yamuna river in Hamirpur, Uttar Pradesh
- Runs over the Malwa Plateau
>>>>>>
Ken River
- Source – Kaimur Range, Vindhya Range, MP
- Ken river joins in Yamuna river near Chila, UP
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Other Right Bank Tributaries of Ganga River
Son River
- Source – Amarkantak Plateau.
- Son river joins Ganga river near Danapur in Patna, Bihar.
- Tributaries – Ghaghar, Johilla, Gopad, Rihand, Kanhar and North Koel.
>>>>>>
Damodar river
- Sourcr – Chotanagpur plateau
- Flows through a rift valley.
- Tributaries – Barakar, Konar, Bokaro, Haharo etc.
- Barakar is the most important tributary of the Damodar.
- Damodar valley is called “the Ruhr of India”.
- It called ‘Sorrow of Bengal’
- It joins the Hugli River 48 km below Kolkata.
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Left Bank Tributaries of The Ganga River
- These rivers originate in the Himalayas.
>>>>>>
Ramganga River
- Source – Namik Glacier, Garhwal, Uttarakhand
- It enters the Ganga Plain near Kalagarh.
- It joins the Ganga river at
- Ganga Dassahra is organised on its banks near Bareilly.
>>>>>>
Ghaghra River
- Source – Mapchachungo Glacier, Manasarovar, Tibet
- Ghaghra river is a trans-Himalayan river.
- It known as the Karnaili river in Western Nepal.
- Tributaries – Kai or Sarda, Sarju (Ayodhya is located on its bank), Rapti
- Ghaghra river joins the Ganga river a few km downstream of Chhapra in Bihar.
- It has a high flood frequency and has shifted its course several times.
Important Tributary of Ghaghara River
Kali River
- It rises in the high glaciers of trans-Himalaya.
- Kali river forms the boundary between Nepal and India.
- It known as the Sarda river after it reaches the plains near Tanakpur.
- Kali river joins Ghaghra River in Uttar Pradesh
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Gandak River
- Source – Nhubine Himal Glacier, Tibet (7,620 m)
- Tributaries – Kali Gandak, Mayangadi, Bari and Trishuli.
- Gandak river joins Ganga river at Hajipur in Bihar.
>>>>>>
Burhi Gandak River
- Source – Chautarwa Chaur, Bihar
- It joins the Ganga river near Khararia town.
>>>>>>
Kosi River
- The Kosi river consists of seven streams namely Sut Kosi, Tamba Kosi, Talkha, Doodh Kosi, Botia Kosi, Arun and Tamber and is popularly known as Saptakoshi
- Seven streams mingle with each other to form three streams named the Tumar, Arun and Sun Kosi.
- They unite at Triveni north of the Mahabharata Range to form the Kosi river.
- Kosi river joins the Ganga river near Kursela, Bihar
- It is often termed as the ‘Sorrow of Bihar’ for frequent flood.
- Embankments for flood control have been constructed as a joint venture of India and Nepal.
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Ganga River Water Treaty
- A temporary water-sharing agreement was signed in 1977 for 5 years.
- The agreement expired in 1982 without being renewed.
- Ganga water sharing had remained a subject of conflict for almost 35 years between India and Bangladesh.
- A comprehensive treaty was signed for a 30-years on 12 Dec 1996.
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
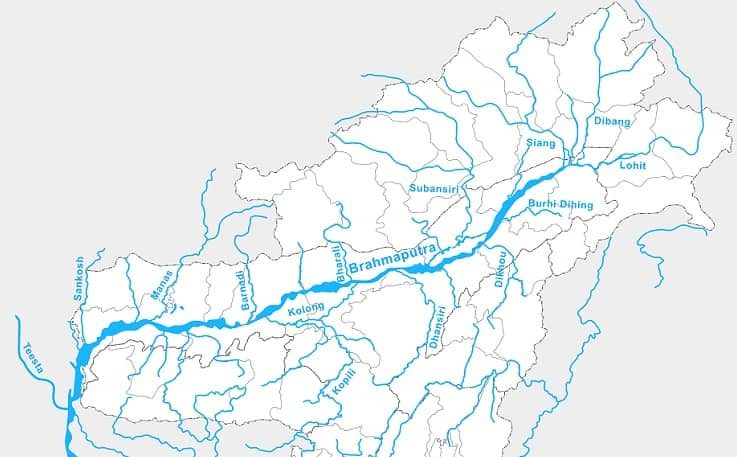
Brahmaputra River
- Source – Chemayungdung glacier, Kailas Range (5,150 m)
- length – 2,900 km
- Left Tributaries – Dibang River, Lohit River, Dhansiri River, Kolong River
- Right tributaries – Kameng River, Manas River, Beki River, Raidak River, Jaldhaka River, Teesta River, Subansiri River (antecedent river)
- Source of Brahmaputra river is very close to the sources of Indus river and Satluj river.
- Mariam La separates the source of the Brahmaputra river from the Manasarovar Lake.
- Name of Brahmaputra river is Tsangpo in Tibet
- Brahmaputra river takes a south ward turn around Namcha Barwa and enter in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Here it first flows under the name of Siong and then as the Dihang.
- Brahmaputra river is joined by two tributaries Dibang from the north and Lohit river from the south.
- From Sadiya (Assam Valley) onwards, it is known as Brahmaputra river.
- The Brahmaputra river is nearly 16 km wide at Dibrugarh and forms many islands, the most important of which is Majuli
- Brahmaputra river bends southwards and enters Bangladesh near Dhubri.
- Its called Jamuna river in Bangladesh.
- The united stream of the Jamuna river and Ganga river flows further in the name of Padma river.
- Padma river is joined on the left bank by the Meghna river.
- Confluence of Padma river and Meghna river, the combined river is known as the Meghna river.
- Tsangpo Grand Canyon in Namcha Barwa is regarded by some as the deepest canyon in the world at (5,500 m).
- Other people consider the Kali-Gandaki Gorge in Nepal to be the deepest canyon, with a 6400 m
>>>>>>
Important Tributaries of Brahmaputra River
Lohit River ( Zayü River)
- Source – Kangri Garpo range, Tibet
- Lohit river joins the Siang (Brahmaputra river) at the head of the Brahmaputra valley
- Longest bridge of India Dhola–Sadiya Bridge (Bhupen Hazarika Setu) 9.15 km constructed on Lohit river.
>>>>>>
Subansiri River
- Source – Himalayas, in China
- Largest tributary of the Brahmaputra river.
- Subansiri river joins the Brahmaputra river in Lakhimpur district and Majuli island created on the mouth of it
>>>>>>
Manas River
- Manas river joins Brahmaputra river at Jogighopa, Assam.
- It is the largest river system of Bhutan.
>>>>>>
Teesta River
- Source – Zemu Glacier, Kangchenjunga, Sikkim
- Tista river was a tributary of the Ganga river befor 1787.
- After a flood it diverted its course eastwards to join the Brahmaputra river.
>>>>>>>