Contents
>>>>>>>
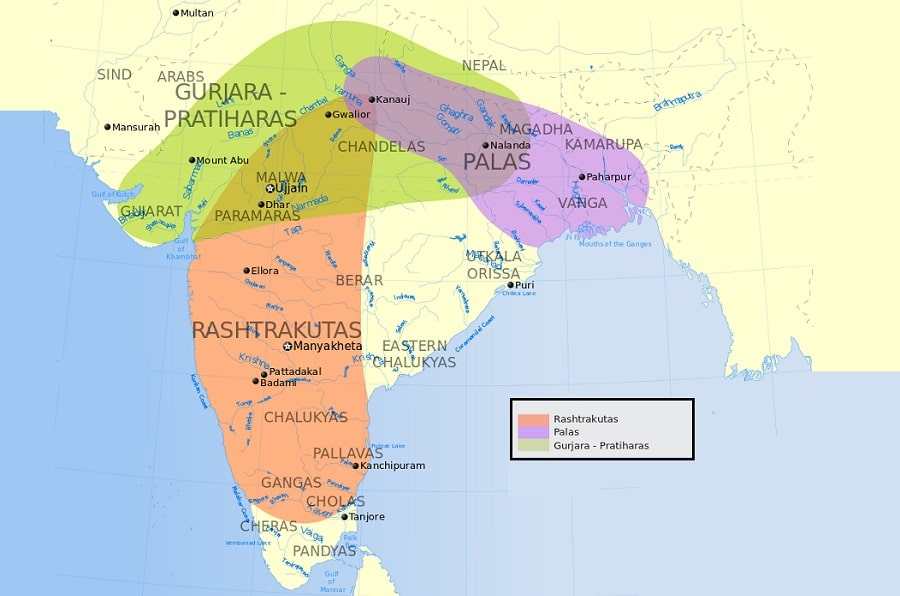
Kannauj Tripartite Struggle
- Kannauj became a point of conflict between three powerful dynasties
- Gurjara Pratihara
- Rashtrakuta dynasty
- Palas
- Kannauj Triangle conflict continued from 8th to 10th centuries.
- The conflict also referred as the Tripartite struggle by many historians.
- The Tripartite struggle began with the defeat of Indrayudh at the hands of Gurjara Pratihara dynasty ruler Vatsaraja.
- Ultimately the Gurjara Pratihara dynasty succeeded in retaining the city.
>>>>>>
>>>>>>
Gurjara Pratihara Dynasty (725-1036)
- The geographical name of Gujarat is supposed to be derived from Gurjara.
- The Gurjara Pratihara dynasty kings were followers of Hinduism.
- The literary meaning of Pratihara is ‘door keeper.’
- It is believed that their ancestor Lakshmana served as a door keeper to his brother Rama.
- They ruled between mid 8th and 11th century A.D. over northern and western India.
- The Pratiharas stood as a fortification of India’s defense against the hostility of the Muslims from the days of Junaid of Sind (725.A.D.) to Mahmud of Ghazni.
- Capital of Gurjara Pratihara dynasty was first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj.
Bhoja
- The Gwalior inscription mentioned the early history of the family founded by King Bhoja in the 7th century.
Nagabhatta I (725-740)
- Nagabhatta is the real founder of the Gurjara Pratihara dynasty
- He established capital at Avanti in Malwa.
- Junaid, another Arab commander defeated by him in Battle of Rajasthan.
Vatsaraja (780–800)
- Vatsaraja captured Kannauj and came in direct conflict with the Palas of Bengal.
- He defeated Dharmapala.
- In 786 AD the Rastrakuta King Dhruva defeated him.
>>>>>>

>>>>>
Nagabhatta II (805-33)
- Nagabhatta was initially defeated by Rastrakuta King Govinda III but later recovered and captured Kannauj.
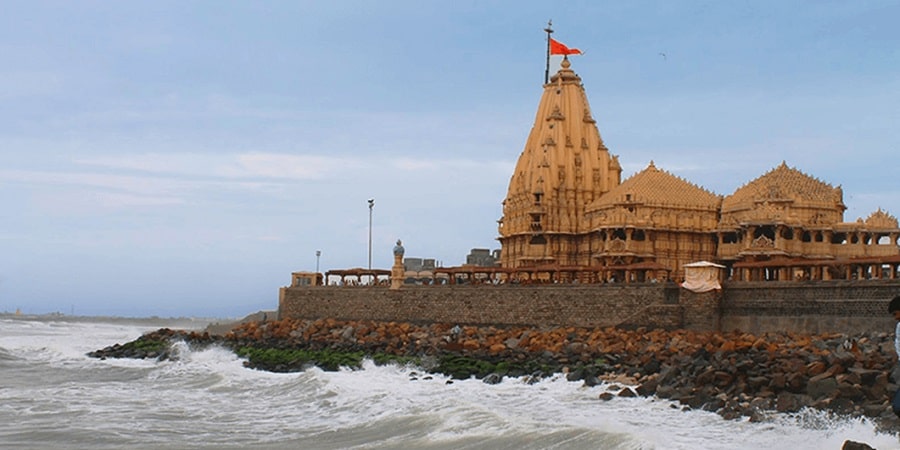
- He is best known for rebuilding the Somnath Temple in 815
- Somnath Temple was destroyed by Arab armies of Junayad in 725 AD.
- This was a large structure of Red Sandstone which was again destroyed in 1024 by Mahamud of Ghazni.
Mihirabhoja (836-85)
- Mihirabhoja defeated Rashtrakuta king Krishna-II and captured the region of Malwa and Gujarat.
- Mihirabhoja was a devotee of Vishnu, and adopted the title of ‘Adivaraha.’
Mahendrapala (885-908)
- Son of Mihirabhoja, was also known as ‘Mahendrayudha’, and ‘Nirbhayanarendra.’
- Rajashehara, Sanskrit poet was in his court.
Mahipala
- Arab scholar, Al-Masudi, visited his court in 915-916.
Decline of the Pratihara Dynasty
- The Rashtrakuta king, Indra-II again attacked Kanauj between A.D. 915 and A.D. 918 and destroyed it.
- Krishna III was other Rashtrakuta ruler invaded north India in about A.D. 963.
- He defeated the Pratihara rulers.
- This led to decline of Gurjara Pratihara Empire.
- Rajyapala was the last Gurjara Pratihara king
- In his time empire was reduced to Kanauj and nearby area.
- The Pratihara power came to an end after Mahmud of Ghazni attacked the kingdom in 1018 A.D.
>>>>>>>

>>>>>>>>
Rashtrakuta Dynasty (755–975 AD)
- Rashtrakuta dynasty called themselves descendants of Satyaki.
- They were a feudatory of the Badami Chalukyas
- Dantidurga overthrew Chalukya king Kirtivarman II
- He built an empire with the Gulbarga region in modern Karnataka as its base.
- This clan came to be known as the Rashtrakuta of Manyakheta, rising to power in South India.
- Rashtrakuta dynasty was Kannada origin and their mother tongue was Kannada or Kanarese.
- Vaishnavism and Saivism flourished during their period.
- Active commerce witnessed between the Deccan and the Arabs.
Dantidurga (735 – 756)
- Dantidurga was the founder of the Rashtrakutas dynasty.
- He occupied all territories between the Godavari river and Vima river.
- Dantidurga occupied Maharashtra by defeating Chalukya King Kirtivarman II.
- From Samangad Plates and Dasavatara Cave of Ellora we can know about his victory
Krishna I (756-774)
- Krishna I succeeded Dantidurga.
- He occupied Konkan coast region.
- Krishna I also defeated Vishnuvardhana of Vengi (Eastern Chalukyas) and the Ganga king of Mysore.
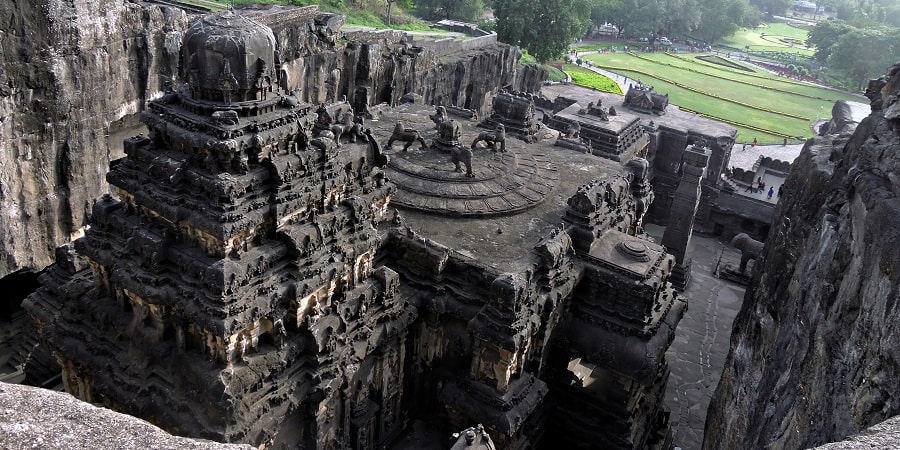
- The Monolithic Kailash Temple at Ellora was built by the Krishna I.
Dhruva (780-793)
- Dhruva defeated Gurjara Pratihara King Vatsyaraja, the Pallavas of Kanchi and the Pala King Dharmapala of Bengal.
- He is the most notable rulers of the Rashtrakut dynasty.
- The Dhulia grant of 779 and Garugadahalli inscription of 782 proclaim Dhruva the emperor.
Govinda III (793-814)
- Govinda III son of Dhruva succeeded the throne.
- The Most successful emperor of the Rashtrakut dynasty
- Govinda III conquered from Cape Comorin in the south to Kannauj in the north, from Banaras in the east to Broach.
- He defeated the great Gurjara King Nagabhatta II.
- Pala King Dharmapala and his protege Charayudh sought the help of Govinda III.
- His kingdom spread up to the Vindhyas and Malava in the north and the river Tungabhadra to the south.
>>>>>>>

>>>>>>>
Amoghavarsha I (814- 878)
- Amoghavarsha I set up a new capital at Manyakheta (now Malkhed in Karnataka State).
- Broach became the best port of the kingdom during his reign
- Amoghavarsha wrote Kavirajamarga, a landmark literary work in the Kannada language
- He was converted into Jainism by Jinasena, a Jaina monk, author of Adipurana.
- Suleman, an Arab merchant, in his account called Amoghavarsha I as one of the four greatest kings of the world.
- Amoghavarsha ruled for 63 years.
Krishna II (878-914)
- Son of Amoghavarsha, succeeded the throne.
- His daughter had married the Chola king Aditya I
Indra III (914 -929)
- Indra III was a powerful king.
- He defeated and deposed Pratihara king Mahipala
- Indra III was married to princess Vijamba of the Kalachuri dynasty of central India (Chedi)
- His Jain general Sri Vijaya (who was also a poet) won may wars for his king
Govinda IV
- He patronised Kannada poet Ravinagabhatta.
Krishna III (939–967)
- The last powerful and efficient king of the Rashtrakuta dynasty.
- He also succeeded in conquering Tanjore and Kanchi.
- Krishna III defeated the Cholas decisively in a battle of Takkolam in the North Arcot district.
- He patronise the famous Kannada poets Sri Ponna, who wrote Shanti purana, Gajankusha, also known as Narayana, who wrote on erotics, and the Apabhramsha poet, Pushpadanta who wrote Mahapurana
- We can know about Krishna III from Atakur inscription
Decline Rashtrakuta Dynasty
- In 972 during the rule of Khottiga Amoghavarsha, the Paramara King Siyaka Harsha attacked and plundered the capital Manyakheta
- The Rashtrakuta King Karka II was defeated and deposed by Taila or Tailapa II, the Chalukya king of Kalyani.
- Indra IV, the last king, committed Sallekhana.
- With the fall of the Rashtrakuta dynasty, their feudatories declared independence.
Rasjtrakuta Dynasty Administration
- Rashtrakuta kingdom was divided into Rashtras (provinces) – controlled by rashtrapatis.
- Rashtras divided into Vishayas or districts, governed by Vishayapatis.
- Subdivision was Bukti, consisting of 50 to 70 villages under the control of Bhogapatis.
- Village headmen carried on village administration.
- Village assemblies played a significant role in the village administration.
>>>>>>>